As a creative marketer, you’re likely on the lookout for innovative ways to reach your audience at all times. There’s a new kid on the block that just might revolutionize interactive marketing, and it’s called image recognition.
While visual recognition enabled by machine learning has been around for awhile, its potential to boost marketers’ efforts is being discovered only lately. Unlike text, which is easily searchable, visual information online has remained a ‘black box.’ But consumers today share an enormous amount of visual data, which marketers struggle to understand.
How can image recognition help you as an interactive marketer?
Image recognition can help brands make sense of the data contained in the ‘visual web.’ Visual listening through machine learning arms marketers with a powerful tool that they’re seeking relentlessly: relevance of content for their audiences.
Because of the technical capabilities it presents, computer recognition of images allows for creative forms of visual storytelling across media too. This offers powerful methods for engaging people and immersing them in new types of interaction with brands. Through effortless profiling based on the social visual content people share online rather than extensive questionnaires, image recognition opens new doors for personalization.

Here are three top ways in which image recognition is bringing unseen advancements for interactive marketing – and how your creative campaigns can hop on the new tech wave.
Visual listening is on the rise for brands
Until recently, a textual understanding of social media and the content shared there by users was the status quo. But with billions of images created and distributed online daily, brands now realize that social listening focusing on text only is ineffective and simply outdated. The rise of visual social networks like Pinterest, Instagram, Snapchat and Tumblr, as well as the wide use of visuals on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn, further pushes this understanding.
Marketers need to analyze enormous quantities of visual material to grasp how people use the currency of ‘visual’ online. While some of them have tried to make sense of images via metadata, this still has not shed enough light on the vast spaces of the visual web.
Enter visual listening. This new method for understanding photos and graphics online is enabled by image recognition AI. It enables brands to mine visual content that their audiences are sharing and engaging with. In this way, they can identify patterns, analyze trends and gain valuable business insights. Marketers can use this data to track how visual posts spread online, what type of visuals gain the most attention, and who is engaging with their visual content. And that’s only the tip of the iceberg.
Simply put, visual listening allows marketers to understand how people consume and create visuals in relation to brands. It provides them with a way to read consumers’ emotions and reactions from the visual data they share. This is also a tool for them to discover and benefit from user generated content that promotes the brand and to identify influencers that can be instrumental in their marketing efforts.
For brand protection, image recognition is a handy tool for monitoring how copyrighted visual material is handled online. Brands can also gain insights into their competitors’ visual presence, which can inform their own campaigns.
With image recognition, personalization can flourish
The applications of image recognition for marketing is not limited to visual listening. In fact, it can fuel powerful personalization, so brands can better reach and engage their audiences.
Creative marketing campaigns based on image recognition analysis can be highly targeted and thus can make a real impact. Through gathering insights from visuals, marketers can learn more about the preferences of different target groups. Based on this, they can craft content that engages people better because it’s relevant and personalized. `Instead of using tedious questionnaires that people avoid, it allows brands to learn more about people’s preferences without asking questions. This is done by analyzing the visual content that users have shared online. It empowers brands to tell engaging stories at the right points of contact with people. KIA Motors created an interactive campaign for 36 lifestyles to match its new KIA K5 (Optima) .
How is image recognition used in the financial industry
The Commonwealth Bank of Australia equipped its mobile app with image recognition software that allows people looking for a new house to take a photo of their dreamed home. By analyzing the picture, the app provides them with information on prices, taxes and other details. Furthermore, the app analyzes their personal financial data to inform them of mortgage options for purchasing the house.
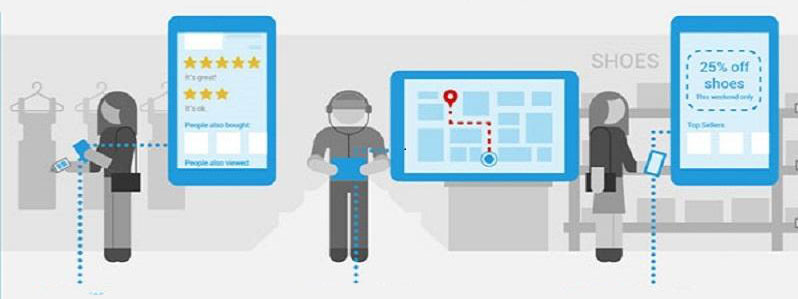
How image recognition created interactive in-store campaigns
Image recognition has a place in the direct shopping experience of consumers by fueling contextual marketing and template matching. Some stores and shopping apps have already integrated image recognition capabilities. People can take a photo of an item they’d like to purchase. Then they receive information about it, locations where they can get it, or even a mobile-optimized page to order it directly.
Big brands like Macy’s and Neiman Marcus have embedded image recognition in dedicated apps. Customers take photos of clothes and accessories they like, and the app automatically suggests items from the brands’ inventory. Other online and brick-and-mortar retailers have also adopted image recognition to engage customers and make their shopping seamless.

A well-known example of image recognition in a consumer app is Vivino. People snap a photo of a wine label to get ratings and details about the brand and sort. The app has turned into a popular helper for making an informed wine choice.
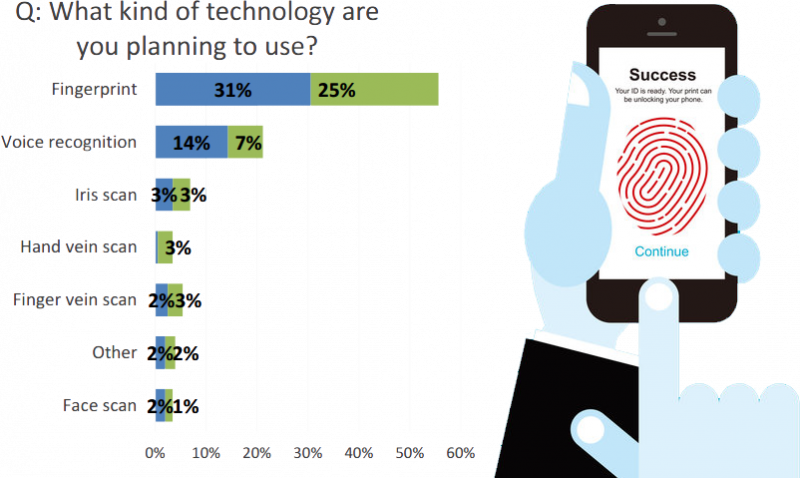
How is image recognition used for access control
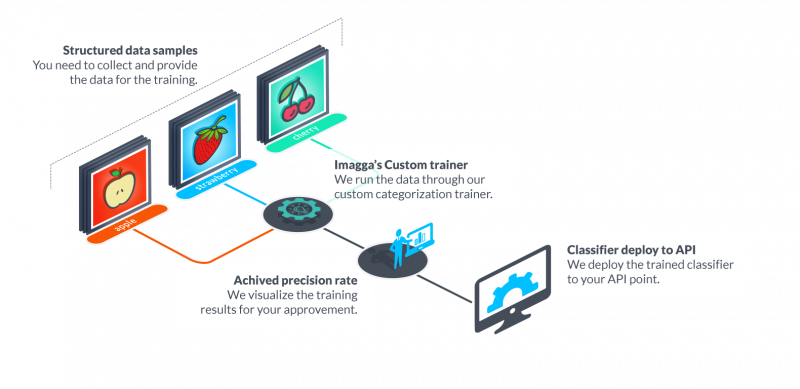
Another cool example of image recognition for an experimental creative campaign is Imagga’s Hipster Bar hack. During the WdW Festival in 2015, the Rotterdam-based artist Max Dovey hosted an installation called the Hipster Bar. Using Imagga’s image recognition, the camera at the door of the bar would take a photo of the person who wants to enter. Then it would juxtapose it against a database of photos of hipsters. If the person matches the style, they’d be able to enter the bar. The concept used for this art case can be applied in a number of marketing purposes. It is based on custom training of the AI by providing it with relevant visual data.
As these three prominent applications of image recognition illustrate, it holds impressive potential for a number of interactive marketing initiatives. Analysis of previously untapped visual data can inform marketers and help them craft powerful campaigns and on-spot content.
Now that you know what image recognition can do for your marketing would you like to give it a try?
