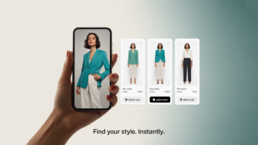
Enable Product Search by Image in Your Platform
In an increasingly visual-first digital world, users don’t want to describe what they see — they want to show it. Visual search bridges that gap, transforming user-uploaded images into powerful discovery experiences. From finding the perfect chair to identifying the kind of rare plants they encounter or surfacing similar products, this technology is changing how people explore and buy online.
And it is not just for end users. It can be incredibly powerful in backend operations. Visual search enables faster product search by matching scanned or photographed items with existing product images in your catalog, making inventory handling more efficient.
If you’re building a platform that needs smart, intuitive product discovery, whether customer-facing or internal, and especially in retail, fashion, furniture, or lifestyle, it’s time to consider adding search by image. Let’s explore how it works, how to implement it using a plug-and-play API like Imagga Visual Search, and the benefits it can deliver for your business.
What Is Visual Search?
Visual search is a technology that allows users to search for information using images instead of text.
At its core, it uses computer vision — a subset of AI that helps machines “see” and interpret visuals. Much like the human eye identifies and recognizes objects that catch your attention, computer vision enables systems to spot and analyze items in images. The system identifies objects, extracts features (like color, shape or texture for example), and compares them to a database to find the most visually similar items.
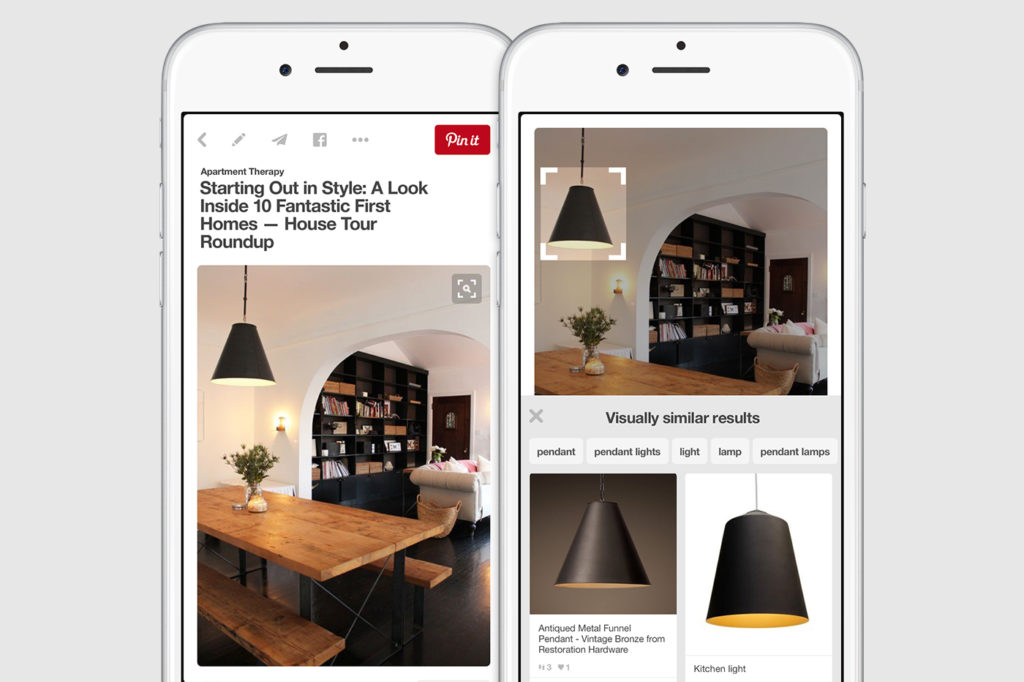
Think of it as reverse image search, but smarter, faster, and purpose-built for product discovery, not just metadata matching.
What’s the difference between reverse image and visual search?
Reverse image search is typically used to find the source of an image or locate exact or near-exact copies across the web. It compares the uploaded image to a database of indexed images, returning matches based on overall similarity or file attributes — tools like Google Images or TinEye are common examples.
Visual search, on the other hand, goes a step further, using advanced computer vision and AI to analyze specific visual features, such as shape, color, texture, and context — and then finds visually similar items, even if they’re not exact matches. This makes the technology ideal for product search, where a user might upload a photo of a chair or outfit and expect to see lookalike products, not just the original image.
In short, reverse image search is about finding the same image; visual search is about understanding and matching what’s in the image so that it can show you visually similar images.
How Your Users Already Use Visual Search (And Why You Should Catch Up)
Your users are already used to this way of finding products — just not on your platform.
Google Lens helps them identify plants, clothes, pets, and restaurants. Pinterest and Amazon let them tap or upload photos to discover similar products. These are some of users' favorite apps for visual search and discovery, offering quick and integrated solutions across devices.
Fashion and furniture brands use it to suggest visually similar styles based on what someone’s browsing.
These platforms have trained users to expect camera-first interaction. If your product discovery still relies on drop-down filters and keyword tags, you’re making users work harder than they should.
Identifying Objects and Products with Visual Search
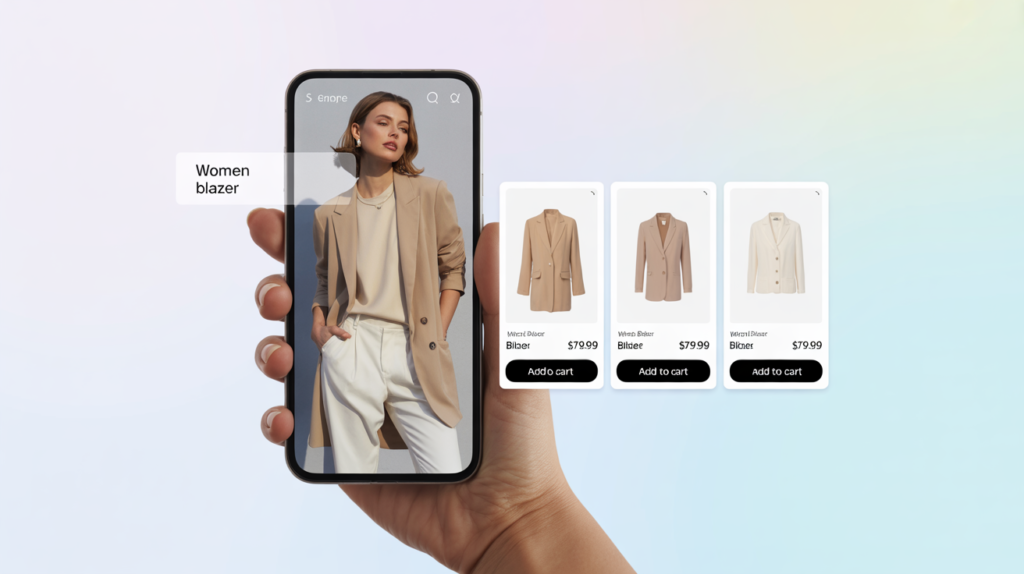
One of the most compelling advantages of the technology is its ability to recognize real-world objects and instantly suggest matches — without the need for perfect descriptions or category filtering.
Whether a user snaps a photo of a chair they saw in a café or uploads an image of a product they own, Imagga’s visual search can identify similar items from your catalog. This goes beyond product titles or metadata — it looks at the actual visual features of the item (like shape, texture, or color) to make a match.
You can use this to:
- Match photographed furniture, clothing, or accessories with similar SKUs
- Help users identify and explore unknown products in your database
- Let internal teams or warehouse staff scan and identify items visually, even without barcodes or tags
- Enable users to identify plants or use animals find features, such as discovering the species of animals they encounter through visual search tools
Visual Search for Product Discovery and Inspiration
Beyond identification, visual search is a powerful tool for serendipitous discovery — especially in verticals like fashion, furniture, and home decor where aesthetics drive decisions.
What is a serendipitous discovery? Serendipitous discovery is the process of unexpectedly finding something valuable or appealing while searching for something else—or nothing at all. In the context of visual search, it refers to uncovering relevant or inspiring products through image-based exploration, even without a clear or specific intent.
With Imagga’s visual search API integrated into your app or website, users can:
- Upload a photo of an outfit and get instant style matches from your product catalog, helping them find the look they want
- Take a picture of a friend's apartment and find complementary furniture or decor, or discover items that match the look of something that catches their eye
Building a Visual Search Backend That Scales
For teams ready to move beyond basic tagging and manual cataloging, Imagga provides the technical foundation for building a powerful, scalable visual product search backend. Unlike general-purpose AI services, Imagga is purpose-built for developers who want tight control over the image-matching process inside their own applications.
Using Imagga’s Visual Search API, you can index your entire product catalog not just by keywords or categories, but by the visual features of each item — color, texture, shape, and more. This allows you to create a backend that responds in real time to user-uploaded images or camera input, returning the most visually relevant products from your catalog.
Product Search Optimization
Optimizing product search with visual tools like Google Lens is transforming the way users interact with the world around them. Instead of typing out long descriptions or struggling to find the right keywords, users can simply open their camera app or upload a photo to instantly search for products, identify plants, or even recognize animals they spot in the park. The Google app, available on select Android devices and all your devices, brings this powerful image search capability right to your fingertips, making it easier than ever to discover details about the things you see every day.
With the product search feature, users can snap a picture of a stylish outfit, a unique chair, or a piece of home decor in a friend’s apartment and quickly find similar clothes, furniture, or accessories online. The Google Lens icon within the app lets you search for products, landmarks, and even dog breeds using just your camera or an image from your gallery. This seamless integration means you can access visual search on your phone, computer, or web browser—whenever and wherever inspiration strikes.
But visual search isn’t just about shopping. The ability to copy and paste text from images means you can quickly find explainers, videos, and answers to homework questions in subjects like math, physics, history, biology, and chemistry. Whether you’re stuck on a tricky problem or want to learn more about a plant you found on a walk, the app helps you access information and learn about the world in a whole new way.
The product search feature is designed to help you check and compare products, making it easy to find the perfect item for your needs—be it furniture, home decor, or clothing. With support for multiple languages and availability in countries like the Netherlands, Google Lens ensures that users everywhere can benefit from smarter, faster product discovery.
By leveraging the power of visual search, you can refine your results, ask questions, and get answers instantly—without having to type a single word. Whether you’re looking to identify a landmark, find the perfect outfit, or solve a science question, the Google Lens app shows you how to use your camera to search, learn, and shop more efficiently. This makes visual search an essential tool for anyone who wants to make smarter decisions and navigate the world with ease.
Visual Search Use Cases (You Can Launch Today)
Here are just a few powerful ways platforms are using visual search:
- Fashion eCommerce: Let users upload a photo of an outfit and see similar styles in your catalog
- Home Decor & Furniture: Snap a picture of a chair, table, or lamp and get lookalike pieces
- Secondhand Marketplaces: Use image matching to clean duplicates and suggest pricing
- Plant/Animal Identification Apps: Recognize species and link to learning resources
- Digital Asset Management: Organize and retrieve visuals using image similarity, not filenames
You can find more real-world examples for visual search applications here.
From Illegal to Harmful: What the DSA & AI Act Mean for Content Moderation
Two key pieces of legislation, the Digital Services Act or DSA and the Artificial Intelligence Act or AI Act are affecting how businesses operate in the digital space. These laws introduce vigorous compliance requirements aimed to create safer and more transparent online environments while providing ethical AI practices. If you run an online marketplace, a social platform, or an AI-driven service, you need to know how these laws impact you - before regulators come knocking.
However, legal texts are dense, full of jargon, and nearly impossible for a business owner to digest quickly. That’s why we’ve invited Maria Catarina Batista, legal consultant, certified data protection officer through the European Center of Privacy and Cybersecurity, as well as certified privacy implementer. Together with Imagga co-founder Chris Georgiev, Maria will translate the implications of the Digital Service Act and the AI Act for online marketplaces, social platforms, and AI-driven services.
The Digital Services Act: Making Online Platforms Safer
The DSA is Europe’s rulebook for making the internet safer, fairer, and more transparent. It applies to online platforms operating in the EU, including social media sites, marketplaces, and search engines. It covers platforms that offer services to users in the EU, regardless of whether the platform is established in the EU or not.
Key obligations:
- Removal of Illegal Content: the DSA requires platforms to expedite the removal of illegal content, such as hate speech, counterfeit goods, and terrorist content.
- Algorithm Transparency: Platforms must provide more transparency regarding their algorithms, especially those used for ad targeting and content recommendation.
- Very Large Online Platforms (VLOPs): Platforms with over 45 million monthly active users in the EU are classified as VLOPs and are subject to stricter obligations under the DSA.
Which businesses are affected by the DSA?
The DSA applies to any company offering intermediary services in the EU, regardless of whether they are established in the EU or not. These services are categorized into:
Mere Conduit Services: internet service providers like Vodafone, which merely transmit data without altering it.
Caching Services: services like Cloudflare, which temporarily store data to speed up access.
Hosting Services: this category encompasses web hosts and cloud storage providers, which store user-generated content.
Online Platforms: social media platforms, e-commerce sites, and search engines.
Very Large Online Platforms (VLOPs): platforms with over 45 million active users in the EU are classified as VLOPs and face additional scrutiny and stricter obligations.
The AI Act: Regulating Artificial Intelligence for Safety and Transparency
The AI Act represents the world's first comprehensive regulation of artificial intelligence, aiming to ensure that AI systems work for the benefit of people, not against them. This groundbreaking legislation seeks to establish a framework that promotes safety, transparency, and accountability in the development and deployment of AI technologies.
Key Takeaways
Classification of AI systems by risk levels
Prohibited AI
The AI Act prohibits the use of AI systems that pose an unacceptable risk to individuals' rights and freedoms. Examples include social scoring systems and certain forms of biometric surveillance that infringe on privacy rights.
High-risk AI
This category includes AI systems used in critical areas such as employment (e.g., hiring tools), law enforcement, and critical infrastructure management. These systems are subject to stringent regulations, including mandatory conformity assessments and registration in an EU database.
Limited-risk AI
This category involves AI systems that require transparency obligations. Examples include chatbots and deepfakes, where users must be informed that they are interacting with AI.
Low-risk AI
Most AI applications fall into this category, which includes systems like AI-enabled video games and spam filters. These are largely exempt from specific regulations but must comply with existing laws.
Obligations for Developers and Deployers
The AI Act places significant responsibilities on developers and deployers of AI systems, particularly those classified as high-risk. They must ensure that their AI systems are fair, transparent, and accountable. This includes providing detailed documentation about the system's development and operation.
Applicability
The AI Act applies to any AI system that impacts the EU, regardless of where it was developed. This means that companies outside the EU must designate authorized representatives within the EU to ensure compliance with the regulations.
Overall, the AI Act sets a new standard for AI governance globally, emphasizing the need for responsible AI development and deployment that prioritizes human well-being and safety.
The AI Act applies to:
- AI Providers: Companies that develop and sell AI solutions.
- AI Deployers: Businesses that use AI to interact with users, make decisions, or analyze data.
- Any AI System Impacting EU Citizens: The AI Act applies to any AI system that affects EU citizens, regardless of where it was developed.
In general the DSA's scope is broader, covering all intermediary services, while the AI Act focuses specifically on AI systems impacting the EU.
Key Legal Challenges and Risks for Businesses
There are several challenges and potential risks for businesses.
Content Moderation: The Fine Line Between Compliance and Censorship
The DSA requires online platforms to remove illegal content swiftly, but this must be done without over-moderating, which could lead to accusations of censorship. This delicate balance is crucial for protecting both user rights and freedom of expression.
One effective approach is to use AI-powered moderation tools combined with human oversight. This ensures that content is reviewed accurately and that decisions are made with a nuanced understanding of context, helping to maintain user trust while complying with regulatory requirements.
Transparency & Algorithm Accountability
The DSA mandates that platforms provide clear explanations about how their algorithms work, particularly those used for content recommendation and ad targeting. This transparency is essential for building trust with users and complying with regulatory demands.
Platforms must offer detailed disclosures about their algorithms, explaining how recommendations and targeted ads are generated. This not only helps users understand why they see certain content but also demonstrates compliance with the DSA's transparency requirements.
3. AI Bias and Explainability Issues
While the DSA does not directly address AI bias, ensuring that AI systems are fair and unbiased is vital for maintaining user trust. The broader regulatory environment, including the AI Act, emphasizes the importance of AI explainability.
Implementing AI explainability frameworks and conducting bias audits can help address these concerns. By providing insights into how AI systems make decisions, businesses can demonstrate fairness and accountability, even if the DSA does not explicitly require this for all AI systems.
Heavy Fines for Non-Compliance
Both the DSA and AI Act impose significant penalties for non-compliance, highlighting the importance of adhering to these regulations.
- DSA Fines: Violations can result in fines of up to 6% of a company's total worldwide annual turnover.
- AI Act Fines: For prohibited AI use, fines can reach up to €35 million or 7% of global turnover (whichever is higher).
- Daily Penalties: Persistent non-compliance under the DSA can lead to daily penalties of up to 5% of global daily turnover.
Best Practices for Compliance with the DSA and AI Act
Ensuring compliance with the Digital Services Act (DSA) and the AI Act requires a proactive and structured approach. Here are some best practices to help businesses navigate these regulations effectively.
- Set Up Strong Content Moderation Mechanisms
Implementing robust content moderation is crucial for compliance with the DSA. Here are some key strategies:
- User-Friendly Reporting Systems: Establish easy-to-use mechanisms for users to report illegal content. This helps ensure that platforms can respond quickly and effectively to user concerns.
- AI Moderation with Human Oversight: Utilize AI-powered moderation tools to streamline the process, but ensure that human reviewers are involved to provide context and oversight. This balance helps prevent over-moderation and ensures that decisions are fair and accurate.
- Detailed Logs for Compliance Audits: Maintain comprehensive records of moderation actions. These logs are essential for demonstrating compliance during audits and can help identify areas for improvement.
2. Improve AI Transparency & Governance
Enhancing transparency and governance in AI systems is vital for compliance with the AI Act and broader regulatory expectations:
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Perform thorough risk assessments for AI systems to identify potential issues and implement mitigation strategies.
- Explain AI Decisions: Provide clear explanations of how AI decisions are made. This transparency helps build trust with users and regulators.
- Regular Bias and Fairness Audits: Regularly audit AI models for bias and fairness to ensure they operate equitably and comply with regulatory standards.
3. Being proactive is key to avoiding compliance issues and potential fines
- Determine Your Business Status: Identify whether your business qualifies as a Very Large Online Platform (VLOP) under the DSA or uses high-risk AI systems under the AI Act. This classification affects the level of regulatory scrutiny and obligations.
- Maintain Detailed Compliance Records: Keep comprehensive records of compliance efforts, including moderation actions, AI audits, and risk assessments. These records are crucial for demonstrating compliance during regulatory audits.
- Internal Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to identify compliance gaps before regulators do. This proactive approach helps address issues promptly and reduces the risk of fines.
- Employee Training: Train employees on AI literacy and legal risks associated with AI and online platforms. Educated staff can help identify and mitigate compliance risks more effectively.
Why Compliance is a Business Imperative?
The DSA and AI Act are just the beginning. The EU is known for influencing global regulations (the “Brussels Effect”), meaning similar laws will likely emerge worldwide.
Key future trends to watch:
- Expanding AI regulations: New AI categories and more stringent compliance.
- Regular updates: The EU will update lists of prohibited AI systems and VLOP designations.
- Stronger penalties: Expect even harsher fines for AI misuse and data privacy breaches.
Understanding and complying with the DSA and AI Act isn’t just about avoiding fines - it’s about building trust, protecting users, and ensuring long-term business viability. As regulations evolve, businesses must stay ahead by investing in transparency, compliance, and responsible AI practices.
For digital platform owners, the choice is clear: adapt now or risk severe consequences.
How can Imagga help?
At Imagga, we offer AI-powered content moderation solutions tailored to your company’s specific needs. Whether you need moderation of images and videos, real-time moderation or AI-assisted workflows our experts can help you stay ahead of regulations while keeping your platform safe.
Learn more about how we can support your business. Or get in touch to discuss your need.
Types of Content Moderation: Benefits, Challenges, and Use Cases
Content moderation is the practice of monitoring and regulating user-generated content on digital platforms to ensure it meets established guidelines and community standards. From social media posts and comments to product reviews and forum discussions, content moderation plays a crucial role in maintaining online safety, preventing the spread of harmful content, and creating positive user experiences. As online platforms continue to grow and evolve, effective content moderation has become essential for businesses and organizations to protect their users, maintain brand reputation, and comply with increasingly stringent digital regulations. In this blog post we'll go through the types of content moderation, the benefits and disadvantages of each and their use cases.
To get a deeper understanding of the fundamentals of content moderation, check out our in-depth guide: What is Content Moderation?
Importance of Understanding Content Moderation Types
Different platforms require different types of content moderation approaches based on their size, content type, and user base. A social media network with millions of active users will require a different strategy than a niche discussion forum. Understanding the various types of moderation allows platform owners to make informed decisions about how to safeguard their communities while ensuring seamless user experiences.
Pre-Moderation
Pre-moderation is a proactive approach where all user-generated content is reviewed and approved before being published on a platform. This method creates a queue of pending content that moderators must evaluate against community guidelines and acceptable content standards before allowing it to go live.
Advantages
This approach provides maximum content control, preventing harmful content and ensuring high-quality standards. It builds user trust by demonstrating a strong commitment to content safety.
Disadvantages
Pre-moderation causes publication delays, limiting real-time engagement. It requires significant human resources, making it costly and hard to scale. The waiting period may also frustrate users, reducing participation.
Use Cases
Ideal for platforms prioritizing safety and quality, such as children’s sites, educational forums, enterprise communication, and healthcare communities. It's also valuable for branded communities, regulated industries, and platforms handling sensitive or confidential topics.
Post-Moderation
Post-moderation is a reactive approach where content is published immediately and reviewed afterward, either through user reports, automated flagging, or routine content audits. This method allows for immediate content visibility while maintaining oversight through subsequent review processes.
Advantages
Supports real-time interaction and engagement by allowing content to flow freely. The post-moderation approach reduces operational bottlenecks, scales efficiently, and is more cost-effective than pre-moderation by focusing on flagged content. Immediate publication keeps users engaged and active.
Disadvantages
Risks exposure to harmful content before removal, which can harm reputation and trust. Problematic content may go viral before moderation teams can act. Post-publication removals can frustrate users and lead to censorship concerns.
Use Cases
Best for high-volume platforms requiring real-time interaction, like social media, news comments, and large forums. Works well with mature audiences and automated filtering. Ideal for fast-paced environments like crisis communication and breaking news discussions.
Reactive Moderation
Reactive moderation is a user-driven approach where content is reviewed only after being flagged or reported by community members. This method relies heavily on user vigilance and community participation to identify potentially problematic content that requires moderator attention.
Advantages
Reactive moderation encourages user involvement, fostering a sense of ownership and shared responsibility. It's cost-effective, requiring fewer moderators, and scales well as user reports grow with content volume. It also highlights issues most relevant to the community.
Disadvantages
Effectiveness depends on user engagement and guideline awareness, which can vary. Harmful content may remain visible until reported. Users may hesitate to report due to fear of retaliation, and malicious reporting can be exploited to harass others.
Use Cases
Best for mature communities with strong self-governance, like professional networks and niche forums. Works well when users understand and support platform standards. Reactive moderation is often used alongside other moderation methods for a balanced approach.
Distributed Moderation
Distributed moderation, also known as community-based moderation, delegates content review responsibilities across a network of trusted community members or volunteer moderators. This democratic approach combines the wisdom of the crowd with structured oversight to manage content at scale.
Advantages
This highly scalable system leverages community expertise to handle large content volumes. It fosters engagement by giving members a role in platform governance and ensures diverse perspectives in content evaluation. Distributed moderation is cost-effective, relying on passionate volunteers instead of paid staff. With moderators across time zones, it provides round-the-clock coverage without the expense of a full-time team.
Disadvantages
Moderation quality can be inconsistent due to individual biases and guideline interpretation. Managing volunteers requires coordination and training, and burnout or turnover can disrupt enforcement. Conflicts among moderators may arise, affecting community stability. Volunteers may also lack the training needed for complex or sensitive moderation decisions.
Use Cases
Ideal for large platforms with distinct subcommunities, such as Reddit or specialized forums. Works well where subject matter expertise is crucial, like technical or knowledge-sharing communities. Effective for platforms with strong community cultures, including gaming communities, open-source forums, and special interest groups with engaged users willing to moderate.
Automated Moderation
Automated content moderation employs artificial intelligence, machine learning algorithms, and rule-based systems to automatically screen, filter, and moderate content in real-time. This technology-driven approach uses natural language processing, computer vision, and pattern recognition to identify and handle potentially problematic content without human intervention.
Advantages
Automated content moderation offers unmatched speed and scalability, processing vast amounts of content instantly. It ensures 24/7 rule enforcement without fatigue or bias, maintaining consistency. These systems handle multiple formats (text, images, video) and languages, making them ideal for global platforms. They reduce reliance on human moderators, cutting costs while improving efficiency. Additionally, AI can detect patterns in violations, helping refine moderation strategies over time.
Disadvantages
AI struggles with context, nuance, and cultural differences, leading to false positives or overlooked violations. It may fail to detect sophisticated rule-breaking tactics that require human judgment. Implementation and maintenance are costly, demanding technical expertise and frequent updates. Users can also learn to bypass automated filters, and excessive reliance on automation may create an impersonal user experience.
Use Cases
Automated moderation is best suited for high-traffic platforms like social media, streaming services, and online marketplaces. Effective for detecting clear violations such as spam, explicit content, and banned material. Works well alongside human moderation, automating routine screening while escalating complex cases. Essential for platforms requiring real-time filtering, such as live-streaming or chat applications, where speed is critical for user safety.
What to Consider When Choosing a Content Moderation Strategy?
Every platform must carefully evaluate its needs before implementing a content moderation strategy. The choice of moderation approach can significantly impact user satisfaction, platform growth, and community health. Several key factors influence this decision:
Platform Size and User Base
Larger platforms rely on automated moderation for scale, with human oversight for complex cases. Smaller platforms may prefer manual moderation to maintain quality while growing. User demographics matter - stricter pre-moderation suits younger audiences, while professional communities thrive with reactive moderation.
Content Type
Content type shapes moderation strategy. Text platforms use NLP for screening, while image and video sites need AI and human review. Live streaming requires real-time moderation, while forums benefit from pre-moderation process. Multi-format platforms often combine approaches for full coverage.
Community Guidelines
Community guidelines shape moderation needs. Strict platforms may require pre-moderation or strong AI filtering, while flexible ones can use post-moderation or community oversight. Complex rules demand more moderator training and refined automation. Clear guidelines for managing users generated content ensure consistent enforcement.
Resource Availability
Budget and resources shape moderation strategy. Automation has high upfront costs but scales efficiently, while human teams need ongoing training and management. Platforms must factor in infrastructure, tools, and expertise in AI, community management, and content policy.
AI Integration in Content Moderation
Advancements in artificial intelligence are transforming content moderation. AI-powered systems enhance efficiency, consistency, and accuracy, enabling platforms to handle vast amounts of content at scale while reducing reliance on human moderators. These technologies help detect and address harmful content more effectively, improving user experience and platform safety.
Machine Learning Algorithms
AI-driven machine learning models continuously refine their ability to detect harmful content by analyzing large datasets. These systems learn from historical moderation decisions, adapting to evolving trends in inappropriate or harmful material. As they process more data, they become better at distinguishing between acceptable content and violations, reducing false positives and negatives. This adaptability makes AI moderation increasingly effective over time, particularly in identifying new forms of harmful behavior, such as emerging slang or disguised hate speech.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows AI to analyze text, detecting hate speech, spam, and misinformation with contextual understanding. It recognizes sarcasm, coded language, and prioritizes flagged content by severity. Essential for moderating social media, forums, and news discussions.
Image and Video Recognition
AI-powered image and video recognition tools analyze visual content to detect explicit imagery, violent content, and other policy violations. These systems can identify nudity, graphic violence, and even manipulated media in images and videos. Advanced models also recognize context, differentiating between harmful visuals and legitimate content, such as medical or educational imagery. By automating visual content moderation, AI significantly reduces the burden on human moderators while ensuring faster and more consistent enforcement of platform guidelines.
Benefits of AI Integration
AI-powered moderation systems offer significant advantages, improving the efficiency, accuracy, and speed of content review processes. By leveraging machine learning, natural language processing, and image recognition, AI helps platforms maintain a safe and engaging environment while reducing the workload for human moderators.
Scalability
One of AI’s biggest strengths is its ability to handle vast amounts of content at scale. Unlike human moderation teams, which are limited by time and resources, AI can analyze millions of text, image, and video submissions simultaneously. This is crucial for large social media platforms, forums, and e-commerce sites, where user-generated content is continuously uploaded. AI ensures that platforms remain manageable even as user engagement grows, allowing businesses to expand without compromising content oversight.
Consistency
AI moderation applies content standards uniformly, reducing the subjectivity and bias that can come with human decision-making. While human moderators may interpret policies differently, AI enforces rules with strict adherence to predefined guidelines. This ensures fair and predictable moderation of harmful content, reducing the risk of disputes over inconsistent enforcement. Platforms benefit from a more reliable user experience where moderation outcomes remain steady across different cases, languages, and regions.
Real-Time Moderation
Speed is essential in content moderation, and AI provides near-instantaneous analysis of content, identifying harmful material the moment it is posted. This rapid response helps prevent the spread of inappropriate content, misinformation, or harmful behavior before it gains traction. AI’s ability to detect and act on violations in real time is especially valuable in live-streaming, chat platforms, and news comment sections, where quick intervention is necessary to maintain a safe and respectful environment.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI-powered moderation offers efficiency and scalability, it also presents challenges that platforms must carefully address. From understanding context to ethical concerns, these issues require a balanced approach that often combines automation with human oversight.
Contextual Understanding
AI struggles with interpreting nuance, sarcasm, and cultural variations in communication. A phrase that is offensive in one context may be harmless or even humorous in another. Language evolves quickly, and AI may misinterpret emerging slang, coded speech, or regional dialects. Without human review, automated systems risk making moderation decisions that feel arbitrary or unfair, potentially alienating users.
False Positives/Negatives
Automated systems are not perfect and may incorrectly flag benign content (false positives) or fail to detect harmful material (false negatives). Overly strict filters can mistakenly remove legitimate discussions, while lenient models may allow inappropriate content to slip through. Striking the right balance requires continuous refinement, user feedback loops, and hybrid moderation approaches where AI flags content for human review in ambiguous cases.
Ethical Implications
AI moderation raises concerns about censorship and user privacy. Overly aggressive content filtering can suppress free expression, leading to accusations of bias or unfair content removal. On the other hand, automated moderation often involves analyzing user-generated content, raising questions about data privacy and surveillance. Platforms must navigate these concerns transparently, ensuring that moderation policies align with ethical guidelines and user rights.
Effective Content Moderation in Action
Imagga AI-driven Content Moderation Platform provides a state-of-the-art solution for online platforms to automatically filter offensive, harmful, and illegal visual content as well as to detect AI-generated visual content. Engineered to meet the trust and safety policies of online platforms, it ensures user protection and mitigates organizational reputational risks. The solution is versatile, deployable in the Cloud, on-premise, or on edge/mobile devices, making it ideal for any platform that needs robust visual content moderation.
Future Trends in Content Moderation
As content moderation evolves, several key trends are shaping the future:
AI and Machine Learning Innovations
Improvements in AI technology will enhance contextual understanding and decision-making accuracy.
User Empowerment Tools
New features will allow users to customize their content experience, offering greater control over what they see.
Regulatory Developments
Governments and organizations will continue refining legal frameworks to address content moderation challenges and responsibilities. Check out our comprehensive guide to content moderation regulations.
Conclusion
Choosing the right moderation strategy is essential for ensuring user safety, content integrity, and platform growth. Whether leveraging AI, community-driven approaches, or human moderators, platforms must strike the right balance between oversight and engagement.
Platforms consider factors such as user base size, content type, and compliance requirements to determine the best moderation strategy.
Yes, many platforms combine different methods, such as AI filtering with human review, to ensure a balanced approach.
Users contribute by reporting violations, participating in distributed moderation, and shaping platform guidelines.
The three main types are pre-moderation, post-moderation, and reactive moderation, each serving different needs and objectives.
What is Video Moderation And Why Digital Platforms Need It
In 2023, the average person spent 17 hours per week watching online video content. Unfortunately, not all of it is appropriate - or even safe - and the problem is only growing. TikTok alone removed nearly 170 million videos from its platform in the first quarter of 2024 due to policy violations.

Find more statistics at Statista
Without proper video moderation, harmful, illegal, or offensive content can spread unchecked, damaging user trust and a platform’s reputation. Research also shows that exposure to violent or harmful content can reduce empathy and increase aggression, anger, and violent behavior.
Watching unmoderated video content is like drinking water from an unfiltered source – the more you consume, the higher the risk of exposure to harmful elements. Just as contaminated water can lead to physical illness, repeated exposure to violent, misleading, or harmful videos can negatively impact mental health, distorting perceptions of reality and increasing aggressive tendencies. Video moderation is especially important for protecting vulnerable groups, such as children, from exposure to inappropriate or harmful content.
If you run a platform with user-generated videos, ensuring safe, compliant, and appropriate content is not just an option – it’s a necessity. But video content moderation is far more complex than moderating images or text. This article explores what video moderation is, how it works, and why it’s critical for digital platforms running user generated content.
What is Video Moderation?
Video moderation is the process of analyzing and managing user-generated video content to ensure compliance with platform guidelines, regulatory standards, and community expectations. It helps digital platforms and businesses maintain a safe, engaging environment by detecting harmful, inappropriate, or non-compliant content, often focusing on the analysis and processing of various media types such as images, videos, audio, and text.
As a subset of content moderation, video moderation is more complex due to its multi-layered nature, requiring advanced tools and cross-modal analysis to assess speech, visuals, and contextual meaning across dynamic formats like live streams and pre-recorded videos. Moderating audio content in videos is especially important, as it requires the ability to review, transcribe, and analyze audio for potential policy violations.
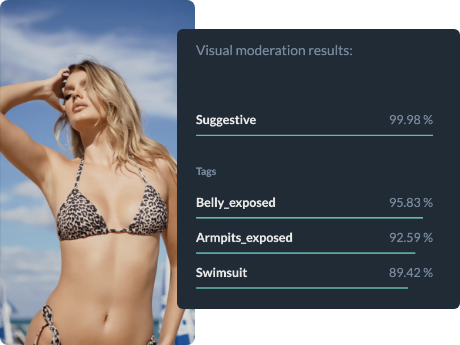
Types of Video Content
Video content on digital platforms comes in many forms, each presenting unique challenges for content moderation. User-generated content is at the heart of most social media platforms, where individuals upload and share their own videos with a global audience. This type of content is dynamic and unpredictable, making it essential for platforms to have robust moderation tools in place to filter out inappropriate content such as hate speech, violence, or adult content.
Live streams are another rapidly growing media type, allowing users to broadcast video in real-time. Moderating live streams requires specialized tools that can detect and respond to violations as they happen, since inappropriate content can reach viewers instantly and cause immediate harm to a platform’s reputation.

Pre-recorded videos, in contrast, offer platforms the opportunity to review and moderate content before it goes public. This allows for more thorough analysis and the ability to apply moderation criteria consistently, reducing the risk of unwanted content slipping through.
No matter the type—user generated, live, or pre-recorded — effective content moderation is essential to ensure that all videos comply with platform rules and community standards. By implementing strong moderation processes, platforms can protect their users, maintain a positive environment, and uphold their brand reputation in the competitive world of social media.
Types of Video Moderation
Automated content moderation relies on AI-powered tools that analyze videos for inappropriate content, such as violence, nudity, hate speech, or misinformation. These systems use machine learning algorithms to scan visuals, speech, and text overlays for violations of platform guidelines. While AI moderation is highly scalable and efficient, it often struggles with understanding context, sarcasm, and nuanced content.
Human moderation involves trained moderators manually reviewing flagged content to ensure compliance with community standards. Unlike AI, human reviewers can assess tone, context, and intent, making them essential for cases that require deeper understanding. However, this approach is labor-intensive, costly, and exposes moderators to mental health issues.
Community moderation is another method where users help flag inappropriate content for review. This is a cost-effective strategy that encourages user participation, but it heavily depends on active engagement from the community and may result in delays before action is taken.
The hybrid approach combines AI automation with human oversight, leveraging the strengths of both. AI handles bulk moderation and flags potential violations, while human reviewers refine the results, ensuring accuracy. Most companies opt for this method to strike a balance between efficiency and reliability. Additionally, human moderators serve a dual purpose. Beyond making decisions where AI falls short, they provide valuable feedback to improve machine learning models over time. By labeling edge cases and correcting AI mistakes, human reviewers help train AI systems, making them more effective and reducing reliance on manual intervention in the long run.
With advancements in AI-powered moderation, companies are increasingly relying on automation to manage video content at scale. A prime example is TikTok, where the percentage of videos removed by automation has steadily increased, reflecting the platform's growing dependence on AI tools to maintain content integrity.

Find more statistics at Statista
Why is Video Moderation Important?
Moderation prevents exposure to harmful content, including violence, exploitation, hate speech, and misinformation, fostering a safe online environment. Platforms must also adhere to GDPR, COPPA, the Digital Services Act, and other regional laws. Failure to comply can lead to fines, legal issues, or even platform shutdowns. Unmoderated content can damage a platform’s reputation, causing user distrust, advertiser pullbacks, and potential bans from app stores. Additionally, video moderation helps filter spam, scams, and inappropriate monetized content, ensuring advertisers remain confident in platform integrity. Moderation also covers user-generated posts, messages, reviews, and comments, which may be limited or removed if they violate platform policies. A well-moderated platform promotes a positive and engaging user experience, encouraging content creators to stay active and attract more users.
Why Video Moderation is More Difficult Than Image or Text Moderation
Video content moderation is particularly challenging because typically each second of video contains 24 to 60 frames, requiring platforms to process thousands of frames per minute. Unlike static images, video requires analysis of moving visuals, background context, speech, and text overlays, making AI moderation more resource-intensive. Moderating live streams adds another layer of complexity, as content must be analyzed and filtered in real-time while the stream is being broadcast to viewers. The cost of moderation also scales with the number of frames per second being analyzed, making AI moderation expensive and human review even more time-consuming.
Additionally, bad actors constantly evolve tactics to bypass moderation filters, such as altering videos, changing speech patterns, or inserting harmful content subtly, further complicating the moderation process.
Artificial Intelligence in Video Moderation
Artificial intelligence has become a game-changer in the world of video moderation. By leveraging machine learning, platforms can analyze vast amounts of video content quickly and accurately, identifying potential issues such as hate speech, violence, or adult content. AI-powered moderation tools are designed to detect unwanted or offensive content in real-time, flagging videos that may violate platform guidelines.
Once a video is flagged, human moderators step in to review the content and make a final decision. This combination of artificial intelligence and human review ensures that moderation is both efficient and nuanced, as human moderators can interpret context and intent that machines might miss. The use of AI not only speeds up the moderation process but also helps protect users from exposure to harmful or offensive content, safeguarding the platform’s reputation.
As moderation tools continue to evolve, the partnership between machine learning and human moderators will remain essential for effective content moderation, allowing platforms to detect and address potential issues before they escalate.
Best Practices for Effective Video Moderation
An effective video moderation strategy involves a combination of AI and human review to balance scalability and accuracy. AI is excellent for bulk moderation, but human oversight ensures that content is interpreted correctly in complex situations. Clear content guidelines should be established to help both AI and moderators make consistent enforcement decisions. Transparency in moderation is also key, ensuring that users understand why content is removed or flagged and providing avenues for appeals or clarifications.
To maintain an efficient moderation system, platforms should invest in regularly updating their AI models to adapt to evolving content trends and moderation challenges. Staying ahead of emerging threats, such as new tactics used by bad actors to bypass filters, is crucial. By continuously monitoring trends and refining moderation policies, platforms can create safer environments for users and content creators alike.
Case Studies and Examples
Many leading companies have successfully implemented video moderation solutions to protect their platforms and users from inappropriate content. For example, YouTube employs a sophisticated combination of AI-powered moderation tools and human reviewers to detect and remove videos containing hate speech, violence, or other offensive content. This approach allows YouTube to efficiently moderate millions of videos while ensuring that nuanced cases receive careful human review.
Another example comes from a social media platform that integrated a video moderation API to monitor live streams. By using advanced moderation tools, the platform was able to detect and flag hate speech in real-time, preventing offensive content from reaching its users and maintaining a safe online community.
These case studies highlight the importance of effective content moderation in today’s digital landscape. By leveraging the right tools and strategies, platforms can protect their users, uphold their reputation, and foster positive online communities.
Safeguarding Platforms and Users with Imagga’s Content Moderation Solution
As harmful, misleading, or inappropriate videos continue to pose risks to user safety and platform integrity, companies need reliable solutions that can scale with demand while ensuring compliance and trust.
Imagga’s AI-powered content moderation solution offers an advanced, scalable approach to tackling the challenges of video moderation. By leveraging cutting-edge machine learning models, Imagga automates the detection of harmful content in video streams, ensuring a safer and more compliant platform.
If your platform relies on user-generated content, now is the time to strengthen your moderation strategy. Imagga’s intelligent moderation tools provide the precision, efficiency, and scalability needed to keep your platform safe and trusted in an evolving digital landscape.
How World Singles Transformed Content Moderation for Their Global Dating Platform
Creating a safe and welcoming space on a global dating platform is no easy task. For World Singles, a leading dating platform, this challenge became more apparent as their user base expanded. With thousands of user-uploaded images and profiles to moderate daily, the traditional manual review process was falling short. It was slow, resource-intensive, and vulnerable to human error.
The Challenge: Keeping Up with User-Generated Content
World Singles needed a solution to handle the massive influx of content uploaded by users. Ensuring that profile photos adhered to platform guidelines and aligned with diverse cultural sensitivities required a level of precision and efficiency that manual moderation couldn’t achieve. On top of that, their team wanted a way to streamline operations and prioritize user safety without sacrificing quality or scalability.
The Solution - AI-Powered Content Moderation Tailored for Dating Platforms
Imagga offered a robust, AI-driven solution designed specifically for the needs of content dating platforms. By automating key aspects of the moderation process they helped World Singles to achieve the following results:
Automated Adult Content Detection
Imagga Adult Content Detection model automatically flagged explicit content, including nudity and other violations of platform rules.
Text Detection
Imagga’s text detection tool bolstered security by identifying images with potentially harmful or inappropriate text. This functionality helped ensure that uploaded photos met platform standards, reinforcing user safety and trust.
Gender and Age Detection
Imagga’s gender and age detection tools offered precise and dependable insights for verifying user profiles. This automated solution not only enhanced the platform's credibility but also speeded up the verification process, boosting user trust in World Singles.
Seamless Integration and Support
Imagga’s tools were built with seamless integration in mind, enabling World Singles to implement the solution effortlessly and with minimal downtime. Throughout the process, Imagga’s support team offered outstanding assistance, ensuring the tools were fully customized to meet the platform’s specific requirements. This tailored approach aligned perfectly with World Singles’ commitment to providing a respectful and enjoyable experience for users worldwide.
Why World Singles Chose Imagga
World Singles selected Imagga because of its proven expertise in content moderation, outstanding performance, seamless integration capabilities, and a dedicated support team that ensured a smooth implementation..
"Imagga’s technology has significantly improved our content moderation process, helping us maintain a high-quality experience for our users. The automation and precision have been game-changers."
Mike Soudée
Founder, World Singles Networks
The Results - Safer Spaces and Happier Users
After implementing Imagga’s solution, World Singles saw remarkable improvements:
Increased efficiency
Automation streamlined the process, allowing moderators to focus on edge cases.
Higher detection accuracy
Harmful content was flagged more consistently, improving overall platform safety.
User Trust & Safety
By leveraging advanced moderation tools, World Singles enhanced user trust and ensured compliance with regulatory standards. These achievements not only elevated the user experience but also bolstered World Singles’ standing as a reliable and culturally sensitive dating platform.
Content Moderation for Dating Sites - The Key to Long-Term Success
In the competitive world of online dating, content moderation is about more than just compliance - it’s a cornerstone of user trust. Platforms like World Singles can’t afford to overlook the importance of managing user-generated content effectively. Imagga’s content moderation for dating sites proved that AI-powered solutions could deliver unmatched accuracy, scalability, and cultural sensitivity. Read more on the power of content moderation for dating sites.
If your dating platform is looking to enhance safety, efficiency, and user satisfaction, it might be time to explore the possibilities of AI-driven moderation.
Ready to transform your moderation process? Get in touch to discuss your needs.
Generative AI Fashion Imagery: Transforming the Future of the Industry
Fashion is evolving, and the next revolution is happening digitally, aka Generative AI Fashion . Generative AI is now capable of producing photorealistic fashion imagery, rivaling traditional photography. But that’s just the beginning—AI is pushing the boundaries further with virtual human models and virtual try-ons, personalized for each shopper. In this post, we explore where fashion imagery stands today, between being fully created through traditional photography and a future where AI-generated visuals make up a significant portion of the content.
International Creative Director Federico Donelli writes in his article on the current state of AI in fashion imaging that the primary criterion for evaluating AI's ability to rival traditional fashion photography is photorealism. With the introduction of Midjourney V.6, he says, the line between AI-generated and traditional photography has become increasingly difficult to discern. By applying the same methodical approach he uses in directing photo shoots to craft prompts for AI-generated images, Donelli achieves impressive results. He notes that the distinction between AI and traditional photography is now remarkably subtle.

In his detailed analysis of other key aspects of fashion photography—such as framing, camera focus, angles, styling, lighting, hair and makeup, setting, and casting—Donelli concludes that the technology is now largely ready for commercial use, especially when paired with skilled post-production and retouching.
The Challenge: Garment Replication via Generative AI
One of the major challenges in applying AI to fashion imaging, as Donelli highlights, is garment replication—the ability to dress subjects in virtual garments that precisely replicate the look and feel of real clothing.
This is an area where our engineering team has recently made significant strides, achieving impressive results.
Generative AI Fashion Virtual Models
Imagga engineers have successfully transformed images of clothes on plastic mannequins into stunning visuals featuring AI-generated human models.

They’ve developed a model that not only showcases how a given dress looks on women of different body shapes and sizes but also how various design variations of the dress appear.

They have even demonstrated how the same dress looks on women of similar body shapes but from different races and age groups.

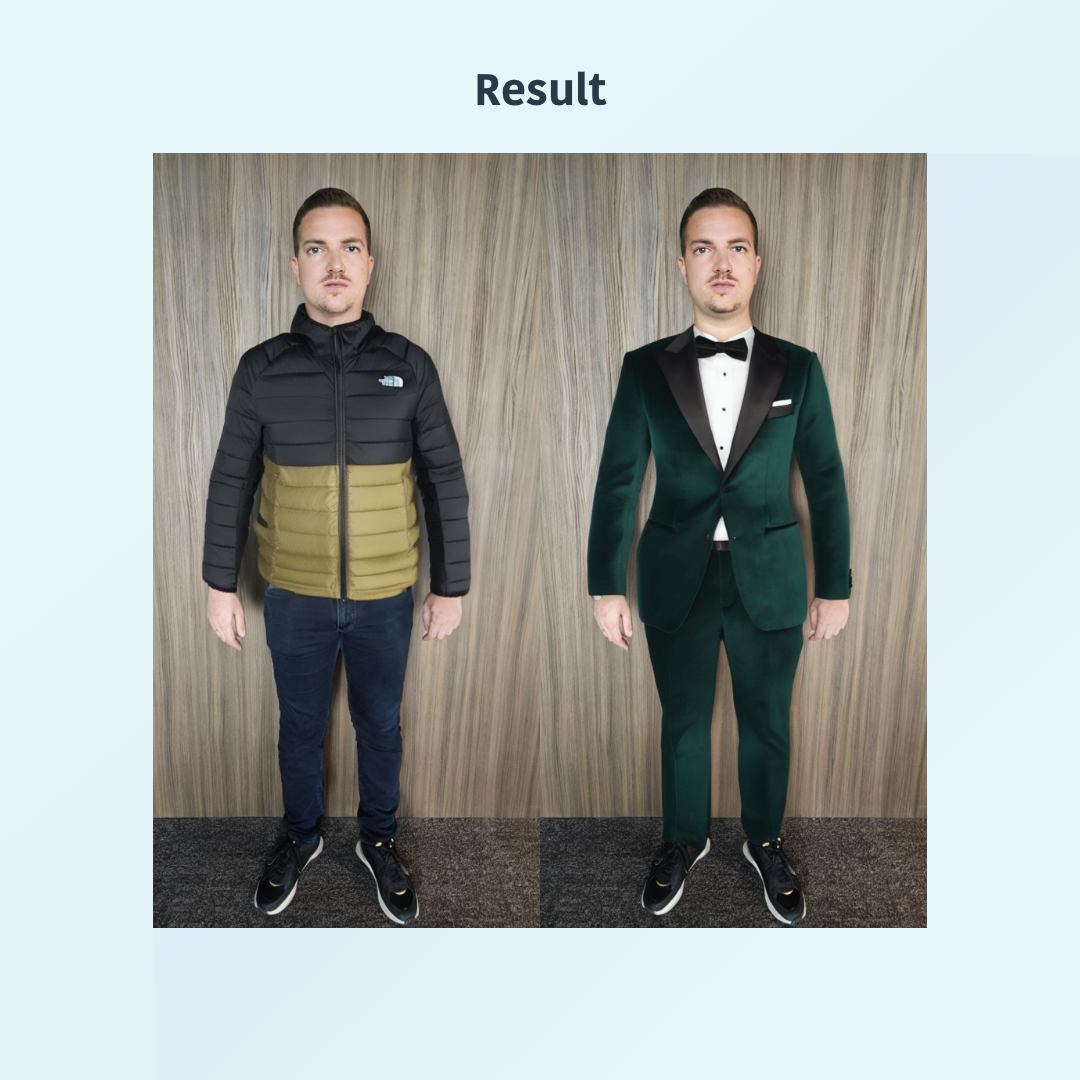
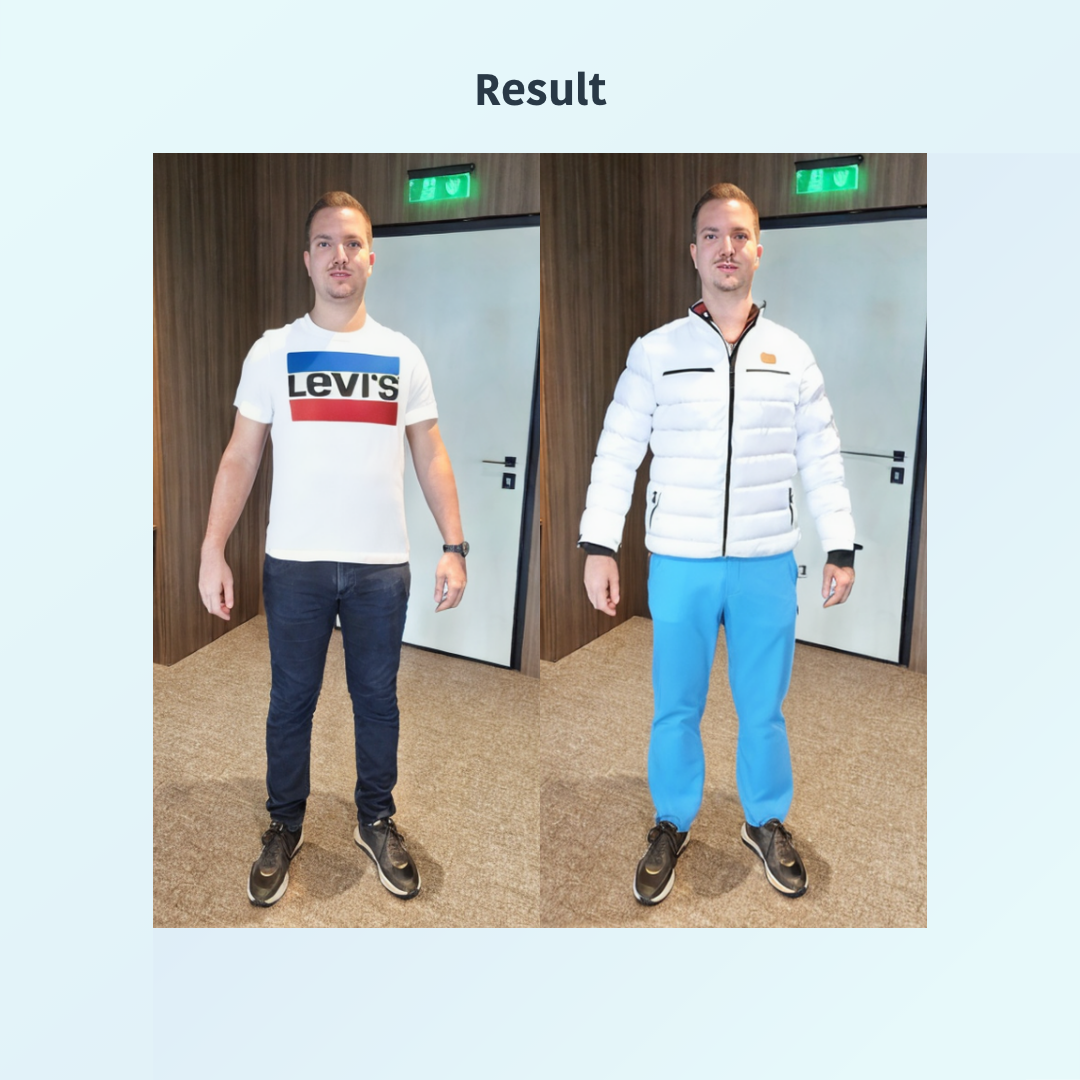
Virtual Try-On
A virtual try-on lets users visualize how clothing would look on them without trying it on physically. It is difficult to build because it requires accurate body simulation, accounting for diverse shapes, sizes, and fabric movement.
Our engineering team has made significant advances with our virtual try-on fashion functionality, which will allow users to upload a photo and see the exact fit on their body, offering a highly personalized and delightful experience.
For online fashion retailers, where user experience is a key differentiator, our virtual try-on has the potential to significantly enhance engagement and conversion rates. By allowing customers to see exactly how clothes will fit using their own photos, it creates a more immersive and personalized shopping experience.
The virtual try-on functionality enhances confidence in online purchases by bridging the gap between virtual browsing and real-life fitting rooms.
 |
 |
 |
 |
The Technology Behind the Generative AI Fashion
Virtual human models are powered by Low-Rank Adaptation Models or LoRA models. These are relatively small machine learning models designed to efficiently adapt and learn from new data. Training LoRA models is the next step toward achieving precision in photorealistic fashion imagery. Image processing algorithms further enhance photo quality by correcting imperfections like glare and color discrepancies.
Implementing generative AI, image processing, and image recognition technologies is no easy task. Here are some of the key challenges:
Skin Tone Accuracy
Accurate representation of skin tone is critical to creating realistic virtual models. Generative AI must be trained on diverse datasets to capture a wide range of skin tones without introducing bias. This requires high-quality data and advanced color calibration techniques to ensure virtual models appear natural under various lighting conditions and on different displays.
Body Posture and Movement
Simulating realistic body postures and movements is particularly challenging. Virtual models must interact with clothing naturally, meaning the AI must understand and accurately replicate fabric dynamics and how they drape over different body shapes. This task demands complex algorithms that predict cloth movement, requiring extensive computational resources and advanced modeling techniques.
Finger and Hand Positioning
Modeling hands and fingers accurately is difficult due to their intricate movements and interactions with objects. Fingers require detailed articulation to avoid unnatural poses that can detract from the overall realism of the virtual model.
Seamless Interaction with Apparel
For a realistic appearance, clothing must conform naturally to the virtual model's body shape. This involves accurately simulating how fabric interacts with body contours, a particularly challenging task with complex garments, such as layered outfits or those made from multiple materials.
Environmental Factors
Achieving photorealism in Generative AI Fashion imagery requires accurate simulation of environmental factors, such as lighting and background elements. Whether it's ambient or direct lighting, these aspects play a crucial role in how clothing appears on virtual models. Properly replicating light sources ensures the images feel natural and realistic. Similarly, background objects need to be rendered in harmony with the scene to avoid distractions and enhance the overall authenticity of the visual.
Scalability and Speed
While creating a few high-quality virtual models is achievable, scaling the process to accommodate thousands of products across various poses and settings is daunting. Ensuring this process remains time- and cost-effective without sacrificing quality is a critical challenge for commercial applications.
The future of Generative AI Fashion
Generative AI is transforming fashion imagery by creating photorealistic images which are virtually indistinguishable from those captured through conventional photography, creating lifelike virtual models and making content production faster and easier. However, there are still big challenges related to garment replication, seamless interaction of models with garments, and scaling the technology for widespread use.
With our deep expertise in image recognition and custom visual model training, combined with ongoing R&D, we’ve developed solutions to help clients bring their ideas to life through advanced AI technologies.
If you’re exploring how AI can enhance your fashion imagery, reach out!

The Myth of Cheap Visual AI: Revealing the True Cost of Advanced Solutions
Artificial Intelligence often gets a reputation for being a cheap, magical solution. AI services like ChatGPT have revolutionized how people interact with technology. For a small subscription fee, anyone can access a powerful language model that can generate text, visual and code. This has led many to believe in the the myth of cheap visual AI - all AI applications share this affordability and ease of use.
General-purpose visual AI models are also budget-friendly and have fueled this belief. They efficiently organize and manage large volumes of images and videos. These models excel when your requirements closely align with their training data; however, their effectiveness diminishes with the specificity of the task such as detecting manufacturing defects or recognizing different types of waste.
The leap from general-purpose models to custom visual AI causes a significant increase in complexity and cost, a reality often overshadowed by the allure of inexpensive AI solutions. In this post, we explore the intricate world of custom visual models designed for complex use cases, shedding light on why they command a higher price tag.
Custom Visual Models: Precision Comes at a Cost
Consider an online fashion retailer that enables customers to upload images of garments they like and search for similar items in its inventory. This capability relies on a finely tuned object detection model and a visual search model, both specialized for this specific use case. Achieving this precision necessitates a comprehensive dataset, including a diverse array of images and detailed attributes like object size, lighting conditions, and background variations. Each nuance adds layers of complexity—and cost—to the models’ development.
The Expertise Required
Developing custom visual AI models is not just a technical challenge; it requires a blend of deep technical know-how and business acumen. The development process is intricate, demanding a multidisciplinary team proficient in computer vision and machine learning, augmented by domain-specific expertise. Moreover, ensuring the ethical use of AI, adherence to data protection laws such as GDPR, and the mitigation of biases is paramount, adding further to the complexity.
The Importance of Quality Data
Data is the cornerstone of any AI model. Custom visual AI models require large quantities of high-quality data that accurately represent the tasks they’re designed for. Often, clients don’t have the necessary data on hand. While this isn’t a dealbreaker for developing the model, it does contribute to rising costs. Data can be collected and annotated in several ways. For example, our partners at Humans in the Loop can assist in data collection and annotation. Additionally, existing datasets can be enriched with synthetic data generation, though this also increases costs.
Is a Custom Visual AI Model Worth the Investment?
Deciding whether to invest in a custom model should start with identifying specific business challenges that visual AI could address. Evaluate whether existing tools are sufficient or if a custom solution could provide a competitive edge. Consider the availability and quality of the data needed to train the model—robust, well-annotated datasets are crucial.
Investing in a custom visual AI solution can be transformative if it uniquely enhances your operations or solves a problem unaddressable by generic models. By understanding the complexities and costs involved, businesses can make informed decisions about harnessing the power of custom visual AI.
Conclusion: Beyond the Hype of Cheap AI
The narrative that AI is universally cheap and easy diminishes the true value and complexity of tailor-made solutions. Custom visual AI models are not just software upgrades—they are strategic investments that require careful consideration and substantial resources. By demystifying the costs and processes involved, we can appreciate the profound capabilities and potential of these advanced technological tools.
Content Moderation for UGC Platforms Guide – Solutions, Infographic, Statistics
What is Content Moderation?
Content moderation is the process of screening and filtering any type of user-generated content (UGC) uploaded and shared online to determine whether it’s appropriate for publication based on predefined rules. The monitored content can be images, videos, audio, text, and livestream. While inappropriate content categories can vary from platform to platform based on the targeted users, there is content that is undoubtedly harmful and illegal and should be blocked no matter the website hosting them.
Billions of people have come online in the past decade, gaining unprecedented access to information. The ability to share their ideas and opinions with a wide audience has grown businesses, raised money for charity, and helped bring about political change. At the same time, the UGC economy has also made it easier to find and spread content that could contribute to harm, like terror propaganda, abuse, child nudity exposure, and others. The free access to content sharing online creates tons of “digital garbage”. Billions of users share text, image, video and audio content online on a daily basis. Some of it is inappropriate, insulting, obscene, or outright illegal. If left unsupervised, user-generated content may cause major harm to brands and vulnerable groups.
“The free access to content sharing online creates tons of digital garbage.”
Companies of various industries and sizes need content moderation as a shield against online bullies. Content Moderation can be performed by people, by AI-powered visual recognition algorithms or by hybrid moderation solutions combining humans and AI.
Why is Content Moderation So Hard?
The complexity of content moderation lies in the enormous volume of UGC and its exponential growth as existing platforms scale and new ones appear. Companies lack the processes and tools to handle the relentless pace at which content circulates on the web. Unlike the content volumes which grow exponentially, the content moderation teams do so at a very slow linear pace. Additionally, the content moderation job is excruciating and has detrimental emotional and mental effects on employees, causing people to quit and content moderation companies to close business.
The alternative solution, AI-powered visual recognition algorithms, while capable to process and filter enormous amounts of content with high precision, cannot deliver where cultural or other context is needed.
Additionally, the margin for error is intolerable. Even if a given platform does a great job filtering 99.99% of the inappropriate content and misses just 0.01%, the missed content (false negative) can do significant damage traumatizing the audience and hurting the company reputation; while the incorrectly blocked unrelated content (false positives) raises issues for censorship.
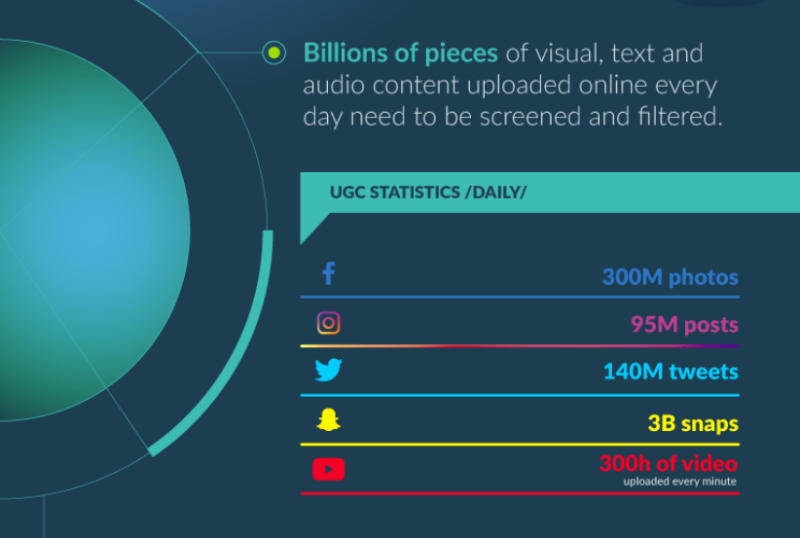
User Generated Content Statistics
Billions of visual, text, and audio content pieces uploaded daily online need to be screened and filtered. Let’s take a look at the number of photos1, videos and tweets shared on some of the biggest social media platforms:
Facebook – 300 million photos uploaded daily
Instagram – 95 million posts daily
Twitter – 140 million tweets daily
Snapchat – 3 billion daily snaps
Youtube – 300 hours of video are uploaded every minute
Who Needs a Content Moderation Solution?
The topic has become a top priority for the largest social platforms amid scandals related to human content moderators’ harsh work reality, escalating content-related crises and increased public and political concerns2.
Тhe reality is that any online platform that operates with UGC is facing the same problem. There will be closer scrutiny on how companies are moderating content as regulators around the globe are paying closer attention to the subject.
Here’s a list of online platform types that need a solution:
- Social media giants like Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, Instagram, Pinterest, Snapchat, Twitter
- Travel and accommodation platforms such as Airbnb and TripAdvisor
- Dating platforms such as Tinder and Grindr
- Entertainment social media such as 9Gag and 4chan
- Artwork communities like DeviantArt and Behance
- Mobile photos and video sharing platforms such as Flickr and 500px
- Stock photography websites such as Unsplash and Pixabay
- Crowdsourcing platforms such as KickStarter and Indiegogo
- Retailers and online marketplaces such as Ebay and Etsy
- Information sharing such as Reddit and Upworthy
- Blog hosting platforms such as Medium and Tumblr
- All blogs and websites that allow user comments in any form, text including
- Audio social networks such as SoundCloud
- Customer review websites such as Yelp
- All marketing campaigns relying on user-generated content
- All online communities and forum websites
Human Content Moderation
Because of the rise of social media, content moderation has become one of the largest and most secretive operational functions in the industry. An army of moderators all over the world screens through the Internet for violence, pornography, hate speech, and piles of inappropriate or illegal content.
There are two major problems with moderation done by people.
The first one is ethical. Evidence keeps piling up, showing that people exposed daily to disturbing and hurtful content undergo serious psychological harm3. Burnout and desensitization are only on the surface, followed by PTSD, social isolation, and depression, according to Sarah T. Roberts, author of Behind the Screen book4. The Verge published an investigation5 into the working conditions at Cognizant in Phoenix, a top content moderation company that later in the same year left that business6. Employees have been diagnosed with post-traumatic stress syndrome.
The other problem is related to productivity and scale but should not and cannot be examined in isolation of the ethical aspect.
- Manual moderation is too expensive and too delayed in time to support near-real-time and live streaming moderation.
- Content volumes grow exponentially while moderation teams do so at a very slow linear pace.
- It’s hard to train huge masses of people and change requirements dynamically, which makes it impossible to change policies or add overnight a new type of content that needs to be recognized
- People overlook things easier than A.I. If a specific piece of content has been flagged as inappropriate, the machine would never mistake it for appropriate again (unless explicitly corrected). This gives the opportunity to stop the spreading of inappropriate content - something that is a major problem for manual moderation
- There is a potential privacy issue when real people examine the content of other real people
“Unlike the content volumes which grow exponentially, the content moderation teams do so at a very slow linear pace.”
AI Content Moderation
AI–powered visual recognition algorithms, or AI content moderation, hold the promise of addressing both the ethical and economic side of the problem. The machine algorithm can do the heavy lifting, processing and categorizing a gigantic amount of data in real-time. It can be trained to recognize visuals in any harmful content category such as pornography, weapons & torture instruments, brawls & mass fights, infamous & vulgar symbols, horror & monstrous images, and many more and achieve an extremely high precision rate.
AI-powered visual recognition algorithms are exceptionally strong at spotting weapons in images and videos, detect nudity or partial nudity, detect infamous people, landmarks, and symbols.
One area where AI models fall short is the contextual understanding of the content and its distribution channels. A video showing an armed conflict between military and civilians might be broadcasted by a TV channel as an important piece of news. But the same video can be viewed as harmful and removed when shared by a user and accompanied by commentary applauding the violence outside of the context in which the violence is being used3.
A Hybrid Solution: Combining the Best of Artificial and Human Intelligence
Combining human judgment with artificial intelligence holds enormous potential for handling the tons of violent, pornographic, exploitative, and illegal content generated online daily. The algorithms, processing the majority of the content, and sending just a small fraction of it to human moderators, can significantly reduce the workload for hundreds of thousands of psychologically harming content moderator positions. Furthermore, it is vastly more productive, easier to scale, and less expensive for companies when most of the data is processed by AI.
As one of the pioneers in the image recognition space, the Imagga data science and engineering teams have deep expertise in developing AI solutions for visual analysis. Learn how Imagga technology is leveraging the best of artificial and human intelligence to handle every aspect of the moderation needs of companies of any size and industry.
Content Moderation Infographic
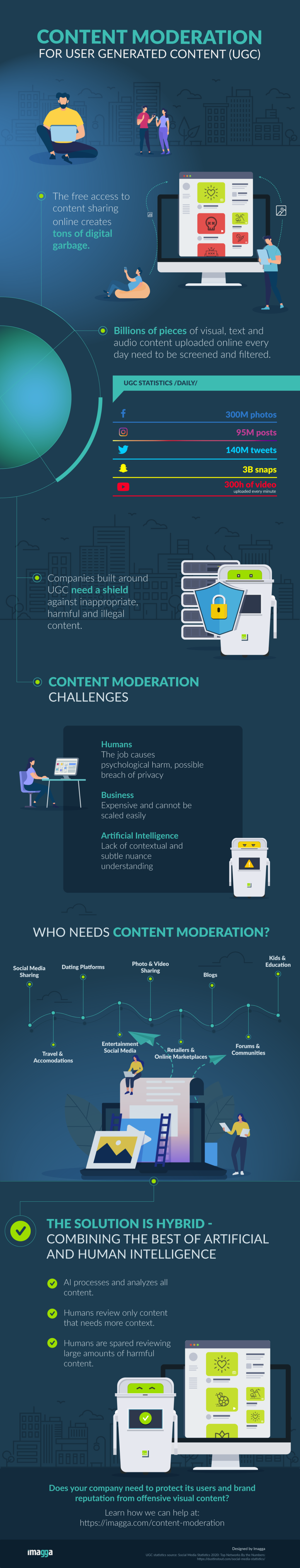
...
Sources:
1. Social Media Statistics 2020: Top Networks By the Numbers: https://dustinstout.com/social-media-statistics/
2. THE CONTENT MODERATION REPORT: Social platforms are facing a massive content crisis — here's why we think regulation is coming and what it will look like: https://www.businessinsider.com/content-moderation-report-2019-1
3. The Problem With AI-Powered Content Moderation Is Incentives Not Technology: https://www.forbes.com/sites/kalevleetaru/2019/03/19/the-problem-with-ai-powered-content-moderation-is-incentives-not-technology/#6caa805c55b7
4. Behind the Screens book: https://www.behindthescreen-book.com
5. The Trauma Floor - The Secret Lives of Facebook Moderators in America: https://www.theverge.com/2019/2/25/18229714/cognizant-facebook-content-moderator-interviews-trauma-working-conditions-arizona
6. Why a Top Content Moderation Company Quit the Business Instead of Fixing its Problems: https://www.theverge.com/interface/2019/11/1/20941952/cognizant-content-moderation-restructuring-facebook-twitter-google
Imagga Joins the Fight Against COVID-19—Develops Software for Early Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases
Kelvin is a platform for monitoring and early diagnosis of infectious diseases that have epidemic/pandemic character.
Our lives are a perpetual transfer of energy - our blood constantly bringing nutrition, protection, and heat to all our organs and body parts. In the intangible but ever-present world of mathematics every single thing in the universe can be described with a mathematical equation. With project Kelvin we unite experts in thermal cameras and optics, image recognition and bio-imaging, respiratory infections and diseases, Big Data and AI/ML analysis, mobile applications development, UI and UX on a mission to protect your and your family’s health by early diagnosis of highly-infectious diseases.
Kelvin works via directly attached thermal-imaging camera to a mobile device (iOS, Android) that feeds image data to a mobile application with an embedded image and medical analysis algorithms.
Our body typically exhibits certain normal temperature deviations in the different body zones. When there’s an inflammatory process, caused by a virus, COVID-19 including, the changes in the deviations can give early signals for a viral infection. The normal thermometers are not capable of detecting these subtle changes, but the thermal cameras are. The image recognition technology developed by Imagga’s team analyzes the personal thermal pictures and the periodic changes in it. Using a specialized algorithm to maximize the accurate assessment of the individual's current state and their respiratory system activity, Kelvin determines the likelihood of a viral infection.
Kelvin utilizes Imagga’s advanced AI technology to address the currently unfolding global crisis due to COVID-19. It can be used by individuals to efficiently monitor their health status (existence and development of infections) in the home environment. The platform can also be used by infected patients to control the inflammation progress, send/receive data to GPs and make timely decisions for hospitalization.
The desired outcomes include virus spread control, monitoring the progress of the disease - stages and complications, opportunity for daily check of the health status of non-hospitalized individuals.
The successful implementation of Kelvin will be of great help to the healthcare systems around the world in the current COVID-19 pandemic situation, allowing the proper prioritization of urgent measures to those who need it most and reducing the unneeded and risky exposure to medical institutions of those who do not.
Project Kelvin is in active development and we’ll provide updates on the progress we’re making.
Image Recognition Explained - Content Moderation
How Are Websites Affected by UK Government Internet Safety Regulations?
With the exponential rise of user-generated content shared online, the need for content screening moderation is increasing. And if until now it was up to the businesses to decide whether they screen content or not, soon they will be required to do so by official content moderation regulations.
The UK government recently announced that Ofcom, the country’s communications regulator, will be put in charge to oversee the internet for two specific areas covering illegal and harmful content. Ofcom will be watching that illegal content is immediately taken down with a particular focus on terrorism and child abuse images, but also prevent the posting of such content in the first place. The organization will also be empowered to fine platforms for user-generated content (UGC) such as social media for serving harmful content to its users.
The proposed legislation yet to be passed but it is clear that it will soon be a reality. With the UK leading the pack, other governments will follow and more companies globally will be affected.
There's a convenient and affordable solution. In this short video, our CEO Georgi Kadrev explains how your company can benefit from an AI-powered content moderation solution.
Any website which published UGC is affected by content moderation regulations
Virtually any website which operates with user-submitted content needs to screen it in order or reduce online harm. And there are many viable reasons for this with or without official legislation in place. The content referred to includes images, videos, and users' comments – thus affecting a large percentage of the online platforms and websites.
What are the options for content moderation?
Content moderation can be performed by humans, AI or both. Companies are still largely relying on human moderation, but this approach is expensive, difficult to scale and takes an emotional toll on the people performing the job. And while AI-powered content moderation addresses both the ethical and economic side of the problem, the algorithms are not yet sophisticated enough to fully take over. In most cases today, the best approach is using both human and AI content moderation – in the most practical and safe ways. Combining the power computer vision and human judgment holds huge potential for moderating a massive amount of violent, pornographic, exploitative and illegal content and protect the internet from online bullies and criminals.
Learn more about Imagga Content Moderation platform.